LogLogisticFitter¶
- class lifelines.fitters.log_logistic_fitter.LogLogisticFitter(*args, **kwargs)¶
This class implements a Log-Logistic model for univariate data. The model has parameterized form:
\[S(t) = \left(1 + \left(\frac{t}{\alpha}\right)^{\beta}\right)^{-1}, \alpha > 0, \beta > 0,\]The \(\alpha\) (scale) parameter has an interpretation as being equal to the median lifetime of the population. The \(\beta\) parameter influences the shape of the hazard. See figure below:
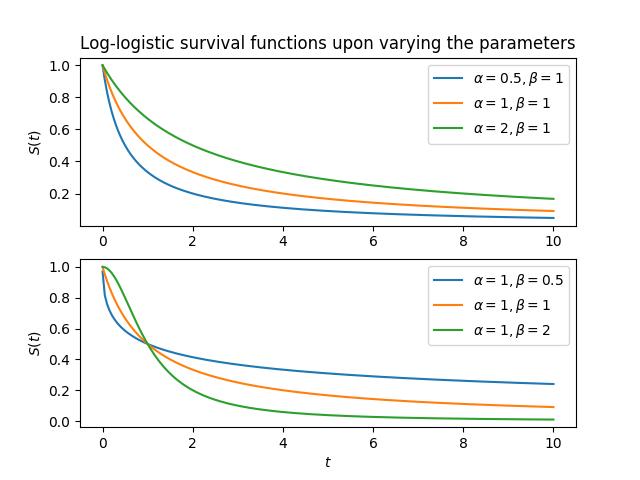
The hazard rate is:
\[h(t) = \frac{\left(\frac{\beta}{\alpha}\right)\left(\frac{t}{\alpha}\right) ^ {\beta-1}}{\left(1 + \left(\frac{t}{\alpha}\right)^{\beta}\right)}\]and the cumulative hazard is:
\[H(t) = \log\left(\left(\frac{t}{\alpha}\right) ^ {\beta} + 1\right)\]After calling the
.fitmethod, you have access to properties like:cumulative_hazard_,plot,survival_function_,alpha_andbeta_. A summary of the fit is available with the method ‘print_summary()’- Parameters:
alpha (float, optional (default=0.05)) – the level in the confidence intervals.
Examples
from lifelines import LogLogisticFitter from lifelines.datasets import load_waltons waltons = load_waltons() llf = LogLogisticFitter() llf.fit(waltons['T'], waltons['E']) llf.plot() print(llf.alpha_)
- cumulative_hazard_¶
The estimated cumulative hazard (with custom timeline if provided)
- Type:
DataFrame
- hazard_¶
The estimated hazard (with custom timeline if provided)
- Type:
DataFrame
- survival_function_¶
The estimated survival function (with custom timeline if provided)
- Type:
DataFrame
- cumulative_density_¶
The estimated cumulative density function (with custom timeline if provided)
- Type:
DataFrame
- density_¶
The estimated density function (PDF) (with custom timeline if provided)
- Type:
DataFrame
- variance_matrix_¶
The variance matrix of the coefficients
- Type:
DataFrame
- median_survival_time_¶
The median time to event
- Type:
float
- alpha_¶
The fitted parameter in the model
- Type:
float
- beta_¶
The fitted parameter in the model
- Type:
float
- durations¶
The durations provided
- Type:
array
- event_observed¶
The event_observed variable provided
- Type:
array
- timeline¶
The time line to use for plotting and indexing
- Type:
array
- entry¶
The entry array provided, or None
- Type:
array or None
- alpha_: float¶
- beta_: float¶
- property median_survival_time_¶
Return the unique time point, t, such that S(t) = 0.5. This is the “half-life” of the population, and a robust summary statistic for the population, if it exists.
- percentile(p)¶
Return the unique time point, t, such that S(t) = p.
- Parameters:
p (float)